JAVA (자바) - 파일 입출력 (txt파일 읽기)
JAVA (자바) - 파일 입출력
원리
1. 파일 객체를 만든다.
2. 해당 파일을 열어 읽는다. (+읽은 내용 알아서 처리, 어디다 쓰든지 문자열을 바꾸던지 뭐 맘대로 하면 된다.)
3. 파일을 닫는다.
1) 한 문자씩 읽기
public class ReadText1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
//파일 객체 생성
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\world\\Desktop\\javaprogramming\\FileIO\\Sample.txt");
//입력 스트림 생성
FileReader filereader = new FileReader(file);
int singleCh = 0;
while((singleCh = filereader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)singleCh);
}
filereader.close();
}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
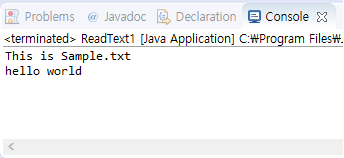
<결과> (Sample.txt 파일에 내용이 결과와 같이 쓰여있었다.)
while((singleCh = filereader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)singleCh);
if((char)singleCh == '\r')
System.out.print("오");
if((char)singleCh == '\n')
System.out.print("아");
}
위에서 while()로 읽는 부분을 변경해보면 윈도우에서 개행문자를 "\r\n"으로 표현하기 때문에 아래와 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다.

* 분명 파일에서는 "\r\n" 두 문자가 개행을 표시하고 자바에서는 "\r"과 "\n" 둘다 개행으로 판단하기 때문에 위와 같은 결과가 나왔구나를 이해할 수 있다.
다만, 그렇게 인식했으면 자바에서 한 문자씩 찍을때 두번 개행이 일어났어야 하는데 의문이 든다. (내 촉은 자바에서 둘이 같이나오면 하나로 처리해주는 것 같다. System.out.print("\r\n"); 이라고 찍어보니까 한번만 개행된다. )
2) 한 줄씩 읽기
package com.tistory.jeongpro;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadText1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
//파일 객체 생성
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\world\\Desktop\\javaprogramming\\FileIO\\Sample.txt");
//입력 스트림 생성
FileReader filereader = new FileReader(file);
//입력 버퍼 생성
BufferedReader bufReader = new BufferedReader(filereader);
String line = "";
while((line = bufReader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
//.readLine()은 끝에 개행문자를 읽지 않는다.
bufReader.close();
}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
기존의 원리에서 벗어나지 않는다.
추가된 내용은 버퍼를 만들어서 한줄씩 읽어 내는 것 뿐이다.
* 파일을 버퍼를 이용해서 읽는 이유는 문자를 효율적으로 입출력하여 CPU부하를 줄일 수 있기 때문이다.
3-1) 파일 한 번에 읽기 - Scanner
package com.tistory.jeongpro;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadText1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
//파일 객체 생성
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\world\\Desktop\\javaprogramming\\FileIO\\Sample.txt");
//스캐너로 파일 읽기
Scanner scan = new Scanner(file);
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(scan.nextLine());
}
//System.out.println(scan.useDelimiter("\\z").next());
}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
Scanner로 한번에 읽었다. Scanner scan = new Scanner(file); 에서 파일을 한 번에 읽어서 스캐너가 가지고 있고
스캐너에 행이 있으면 그행을 하나씩 출력하는 내용이다.
3-2) 파일 한 번에 읽기 - File
파일 쓰기
package com.tistory.jeongpro;
import java.util.List;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ReadText1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//파일 객체 생성
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\world\\Desktop\\javaprogramming\\FileIO\\Sample.txt");
// 캐릭터셋 지정
Charset cs = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
//파일 내용담을 리스트
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
try{
list = Files.readAllLines(path,cs);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(String readLine : list){
System.out.println(readLine);
}
}
}
1) 버퍼를 이용한 파일에 쓰기
package com.tistory.jeongpro;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadText1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
//파일 객체 생성
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\world\\Desktop\\javaprogramming\\FileIO\\Writer.txt");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
if(file.isFile() && file.canWrite()){
//쓰기
bufferedWriter.write("문자열 추가1");
//개행문자쓰기
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.write("문자열 추가2");
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
새로운 파일(Writer.txt)를 만들고 그 파일에 문자열을 추가했다.
Tip. 운영체제 별로 다른 개행문자 처리하기
- 리눅스(유닉스계열)에서 파일 읽었을 경우
String line = System.getProperty("line.separator");
str = str.replace("\n", line);
'⚙️ Backend > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA(자바) - 클래스와 객체 (0) | 2020.11.09 |
|---|---|
| JAVA(자바) - 객체 지향 개념 (0) | 2020.11.08 |
| JAVA (자바) - Literal 리터럴 (0) | 2020.11.03 |
| JAVA (자바) - Operator 문제 제시 (1~14) (0) | 2020.11.03 |
| JAVA(자바) - 함수 (0) | 2020.11.01 |

댓글