MAC / Windows 이클립스 스프링, 오라클 연동, 마이바티스, log4jdbc 라이브러리 사용하기
스프링 오라클 연동
JDBCTests.java 생성
JDBC 연결
package com.koreait.persistence;
import static org.junit.Assert.fail;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) // 테스트 코드가 스프링을 실행
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml") // 지정된 클래스나 문자열을 이용해서 필요한 객체들을 스프링 내에 객체로 등록
@Log4j
public class JDBCTests {
static {
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testConnection() {
// try(Statement) : 소괄호 안에 close를 필요로하는 인스턴스를 작성하면 자동으로 close()를 실행해 준다.
try(Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1600:XE",
"hr",
"hr")){
log.info(conn);
}catch(Exception e) {
fail(e.getMessage());
}
}
}리스너 오류 발생시
서비스 및 응용 프로그램에서 서비스부터 키고, 리스터 키면됨
root-context.xml
커넥션풀 hikari 객체화
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- Root Context: defines shared resources visible to all other web components -->
<bean id="hikariConfig" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig">
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1600:XE"/>
<property name="username" value="hr"/>
<property name="password" value="hr"/>
</bean>
<!-- DataSource dataSource = new DataSource(hikariConfig) -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<constructor-arg ref="hikariConfig"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- ① -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.koreait.sample"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
pom.xml 추가 Test부분
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com.artifact/com.zaxxer/HikariCP -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency> DataSourceTests.java
package com.koreait.persistence;
import static org.junit.Assert.fail;
import java.sql.Connection;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) // 테스트 코드가 스프링을 실행
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml") // 지정된 클래스나 문자열을 이용해서 필요한 객체들을 스프링 내에 객체로 등록
@Log4j
public class DataSourceTests {
@Setter (onMethod_ = @Autowired)
private DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void testConnection() {
try(Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {
log.info(conn);
}catch (Exception e) {
fail(e.getMessage());
}
}
}mybatis 추가
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>mybatis 객체화 root-context.xml
수정 후 메이븐 업데이트 할 것.
<!-- DataSource dataSource = new DataSource(hikariConfig) -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<constructor-arg ref="hikariConfig"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 생성자 프로퍼티, dataSource 참조-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
DataSourceTests.java 연결 테스트
package com.koreait.persistence;
import static org.junit.Assert.fail;
import java.sql.Connection;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) // 테스트 코드가 스프링을 실행
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml") // 지정된 클래스나 문자열을 이용해서 필요한 객체들을 스프링 내에 객체로 등록
@Log4j
public class DataSourceTests {
@Setter (onMethod_ = @Autowired)
private DataSource dataSource;
@Setter (onMethod_ = @Autowired)
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Test
public void testConnection() {
try(SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
Connection conn = sqlSession.getConnection()){
log.info(conn);
log.info(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
fail(e.getMessage());
}
}
// @Test
// public void testConnection() {
// try(Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {
// log.info(conn);
// }catch (Exception e) {
// fail(e.getMessage());
// }
// }
}인터페이스 하나를 만들 것이다.
조인이라는 메소드를 인터페이스로 만든다. 메소드랑 xml이랑 태그의 아이디가 똑같으면 자동으로 들어간다. 자동으로 주입이 된다. 인터페이스 메소드를 사용만하면 DB Query가 완성된다.
root-context.xml에서 Namespaces에서 체크

프로젝트 BuildPath
log4jdbc-log4j2 적용
MyBatis는 내부적으로 JDBC의 PreparedStatement를 이용해서 sql을 처리한다.
따라서 SQL에 전달되는 파라미터는 JDBC에서와 같이 '?'로 치환되어 처리된다.
복잡한 SQL의 경우 '?'로 나오는 값이 제대로 되었는 지 확인하기 쉽지 않고 실행된 SQL의
내용을 정확히 확인하기 어렵기 때문에 log4jdbc-log4j2라이브러리를 사용하여 어떤 값인지를
정확히 확인한다.
ID와 PW를 노출하지 않기 위해
properties를 추가한다.
파일명 src/main/resources/log4jdbc.log4j2.properties
log4jdbc.spylogdelegator.name=net.sf.log4jdbc.log.slf4j.Slf4jSpyLogDelegatorpom.xml 140번줄 쯤 dependecies 안에 추가
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.bgee.log4jdbc-log4j2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bgee.log4jdbc-log4j2</groupId>
<artifactId>log4jdbc-log4j2-jdbc4</artifactId>
<version>1.16</version>
</dependency>
root-context.xml
기존 것을 아래코드와 같이 변경한다.
<property name="driverClassName" value="net.sf.log4jdbc.sql.jdbcapi.DriverSpy"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:log4jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1600:XE"/>

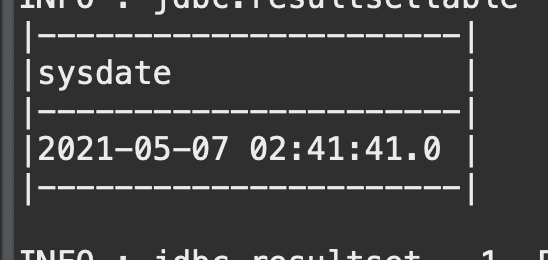
이클립스 콘솔에서 보기 편하게 테이블 구조로 나오게 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
'⚙️ Backend > 스프링(Spring) Framework' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스프링(Spring) - 예외처리, 500 오류 (@ControllerAdvice) (0) | 2021.05.10 |
|---|---|
| (Spring MVC) Front-Controller 패턴 (0) | 2021.05.07 |
| 스프링 - Oracle TimeMapper 예제 (0) | 2021.05.07 |
| MAC / Windows OS 스프링 STS 이클립스 Market Place 설치, 환경 설정 (0) | 2021.05.06 |
| 스프링 - 프레임 워크란? 특징, 장점, 라이브러리 개념 등 (0) | 2021.05.06 |

댓글